Abstract
Background: Despite a variety of treatment options, indolent non-Hodgkin's lymphoma (iNHL) remains a largely incurable disease with patients experiencing multiple relapses. Both rituximab (RTX) and bendamustine (Benda) are used as single agents for the treatment of relapsed/refractory iNHL. When given in combination to patients with relapsed iNHL, high response rates were observed (Rummel, 2016). Ofatumumab (OFA) is a human, anti-CD20 type-I antibody that binds a distinct epitope from RTX. A phase I/II study showed that OFA has activity in patients with follicular lymphoma (FL) who relapsed after RTX-containing therapy (Hagenbeek, 2008). Based on these experiences, COMPLEMENT A+B evaluated if OFA+Benda would improve progression-free survival (PFS) compared to Benda alone in unresponsive or progressive iNHL after RTX or RTX-containing regimen.
Methods: This phase III, open-label, randomized, global, multi-center study enrolled adult patients (≥18 years) with CD20+ small lymphocytic, marginal zone, lymphophasmacytic and Grades 1-3A FL who had either stable disease after or disease progression during or within 6 months of RTX or RTX-containing regimen. Patients were randomized (1:1) to receive either OFA+Benda or Benda. Benda (90 mg/m2 in OFA+Benda arm and 120 mg/m2 in Bendaarm) was given on Days 1 and 2 every 21 days for up to 8 cycles. OFA (1000 mg) was given on Day 1 of Benda cycles and then every 28 days for a total of 12 doses. The primary endpoint was PFS as assessed by an independent review committee (IRC). Key secondary endpoints included PFS in patients with FL, overall response rates (ORR) and overall survival (OS) in all patients and in patients with FL which were tested hierarchically if the prior endpoint was statistically significant.
Results: Overall, 346 patients were enrolled (173 in each arm) in 85 centers across 15 countries. Baseline characteristics were similar between the 2 arms. Median (range) age was 62 (21-87) years, majority were males (59%) and 69% had FL. Ann Arbor Stage IVA was common (OFA+Benda: 43%; Benda: 42%). Median duration of follow up was 61.1 months. Median treatment duration was longer in the OFA+Benda arm (OFA+Benda: 260 days; Benda: 135 days). Median (range) number of prior RTX therapy was 1 (1-8).
In the OFA+Benda arm, 58% and 65% completed treatment with OFA and Benda, respectively, whereas in the Benda arm, 43% completed treatment. The main reason for premature discontinuation of OFA treatment in OFA+Benda arm was adverse events (AEs), 14%. The main reason for premature treatment discontinuation of Benda was AEs (OFA+Benda: 17%; Benda: 27%).
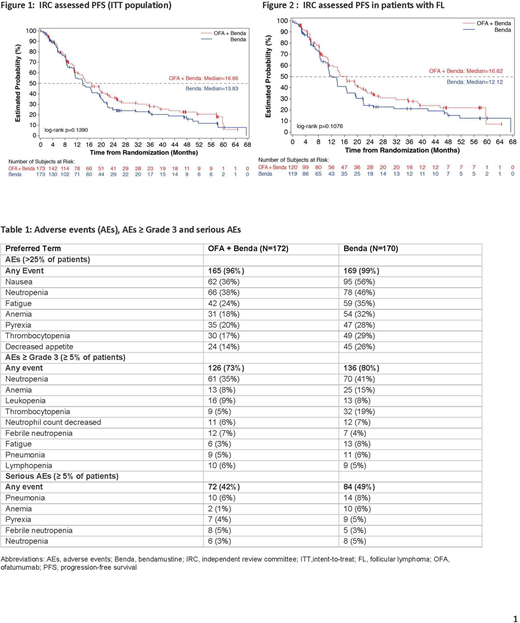
Primary analysis was performed after 217 IRC-assessed PFS events occurred. In the OFA+Benda and Benda arms, 61% and 65% of patients, respectively, had PFS events (Figure 1). Median IRC-assessed PFS was 16.7 months in the OFA+Benda arm and 13.8 months in the Benda arm (hazard ratio [HR]=0.82, 95% confidence interval [CI] [0.62, 1.07]; p=0.1390). Similar results were seen in patients with FL where the median IRC-assessed PFS was similar in FL patients - 16.6 months in the OFA+Benda arm and 12.1 months in the Benda arm (HR=0.76, 95% CI [0.55,1.06]; p=0.1076) (Figure 2). IRC-assessed ORR was similar in both arms (OFA+Benda: 73%; Benda: 75%; difference in ORR [95% C]: -1.2% [-10.4%, 8.1]; p=0.8003). Median OS was 58.2 months and 51.8 months in the OFA+Benda and Benda arms, respectively (HR=0.89, 95% CI [0.63, 1.25]; p=0.4968). Frequencies of deaths (OFA+Benda: 38%; Benda: 41%) and on-treatment deaths (OFA+Benda: 7%; Benda: 9%) were similar in both arms. The main cause of death during the study was disease under study (OFA+Benda: 20%; Benda: 15%). Overall, 73% of patients in the OFA+Benda arm and 80% in the Benda arm experienced a ≥ Grade 3 AE. The most common ≥ Grade 3 AEs were neutropenia, thrombocytopenia, anemia, and leukopenia (Table 1).
Conclusions: No significant improvement in PFS was seen with OFA+Benda as compared with Benda alone for patients with RTX-refractory iNHL. The safety profile for OFA was consistent with prior experience. The difference in outcomes compared to those in the GADOLIN trial (Sehn, 2016) could be due to the differences in drug exposure as patients in the GADOLIN study received maintenance anti-CD 20 therapy for up to 2 years; in the patient population as approximately 80% had FL in GADOLIN versus 69% in COMPLEMENT A+B; and in the mechanism of action of type-1 versus type-2 monoclonal antibody.
Rummel:Mundipharma: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Gilead: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Janssen: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Roche: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Symbio: Honoraria; Celgene: Honoraria; Amgen: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Astellas: Honoraria; Eisai: Honoraria. Janssens:Sanofi-Genzyme: Speakers Bureau; Abbvie: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Other: Ad board, Speakers Bureau; Janssen: Consultancy, Speakers Bureau; Roche: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Other: Ad board, Speakers Bureau; Amgen: Consultancy, Speakers Bureau; Novartis: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees. MacDonald:Roche Canada: Honoraria; Abbvie: Honoraria; Janssen: Honoraria; Merck: Honoraria. Keating:Bayer: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees. Davis:Novartis: Employment. Lasher:Novartis: Employment. Lobe:Novartis: Employment. Izquierdo:Novartis: Employment, Equity Ownership. Friedberg:Bayer: Honoraria.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal